Automated Industrial Systems
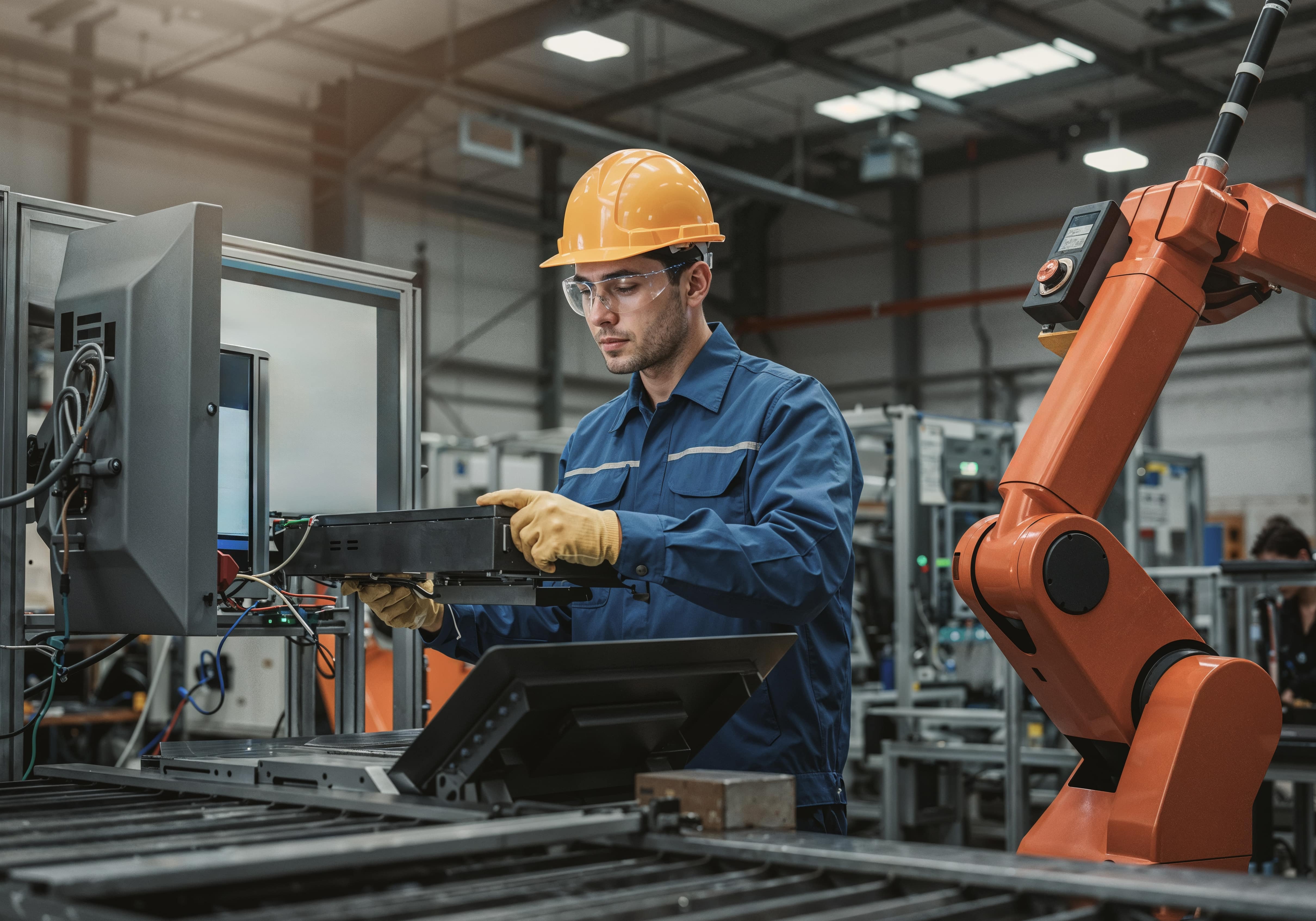

Automated industrial systems are transforming how industries operate, making processes faster, more accurate, and highly efficient. By integrating machinery with intelligent control systems, these technologies reduce human error, improve safety, and increase productivity. As global competition intensifies and labor costs rise, automation is no longer optional—it’s essential.
From assembly lines and packaging to data monitoring and predictive maintenance, automated industrial systems are now the backbone of advanced manufacturing, food processing, energy production, and countless other industries.
What Are Automated Industrial Systems?
An automated industrial system consists of interconnected hardware and software components designed to perform specific tasks with minimal human intervention. These systems often include:
-
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) for executing control logic
-
Sensors and Actuators for real-time input/output communication
-
Human Machine Interfaces (HMIs) for operator control and feedback
-
SCADA Systems for large-scale monitoring and control
-
Robotics for material handling and precision tasks
-
Network Infrastructure for seamless data exchange
These technologies work together to ensure smooth, continuous operations, whether in a small plant or a large-scale industrial facility.
Benefits of Automated Industrial Systems
-
Increased Productivity
Automated systems operate 24/7 without fatigue, resulting in significantly higher output compared to manual processes. -
Improved Accuracy and Consistency
Machines perform tasks with high precision, reducing defects and ensuring uniform product quality. -
Reduced Operational Costs
While initial investment may be significant, automation lowers long-term labor and waste costs, providing excellent ROI. -
Enhanced Safety
Dangerous tasks can be automated to protect workers from hazardous environments. -
Data-Driven Insights
Real-time data collection and analysis lead to better decision-making and predictive maintenance strategies. -
Scalability and Flexibility
Automated systems can be quickly adapted to meet new production demands or product changes.
Common Applications in Industry
Automated industrial systems are used across various sectors to streamline operations and boost efficiency:
-
Manufacturing: Automated assembly lines, CNC machinery, and robotics integration
-
Food and Beverage: Batch processing, packaging, and quality inspection
-
Pharmaceuticals: Precision dosing, cleanroom operations, and documentation compliance
-
Oil and Gas: Drilling automation, pump monitoring, and leak detection
-
Water Treatment: Chemical dosing systems, pump control, and remote SCADA management
-
Logistics & Warehousing: Automated sorting, palletizing, and storage retrieval systems
The Role of System Integration
Implementing automated industrial systems requires more than just installing new machines—it involves carefully integrating multiple technologies into a seamless workflow. This is where expert automation engineers come into play. System integration includes:
-
Designing the automation architecture
-
Programming PLCs and configuring HMIs
-
Ensuring communication between devices and platforms
-
Testing and validating system performance
-
Providing ongoing maintenance and technical support
For businesses looking to maximize automation efficiency, working with skilled professionals is essential.